Myocardial Ischemia:
Myocardial Ischemia manifests as an inadequate supply of oxygenated blood to the heart muscle, suffocating it in a dire embrace. This suffocative grip results from a gradual narrowing of the coronary arteries, stemming from the aggregation of arterial plaques. Such an intricate tapestry of pathophysiology places immense pressure on medical professionals to unravel its mysteries and forge a path toward elucidation. The allure of Myocardial Ischemia lies in its ability to exhibit varied facets, leaving even seasoned diagnosticians perplexed. The clinical presentation often takes the form of angina pectoris, a discomforting sensation coursing through the chest.
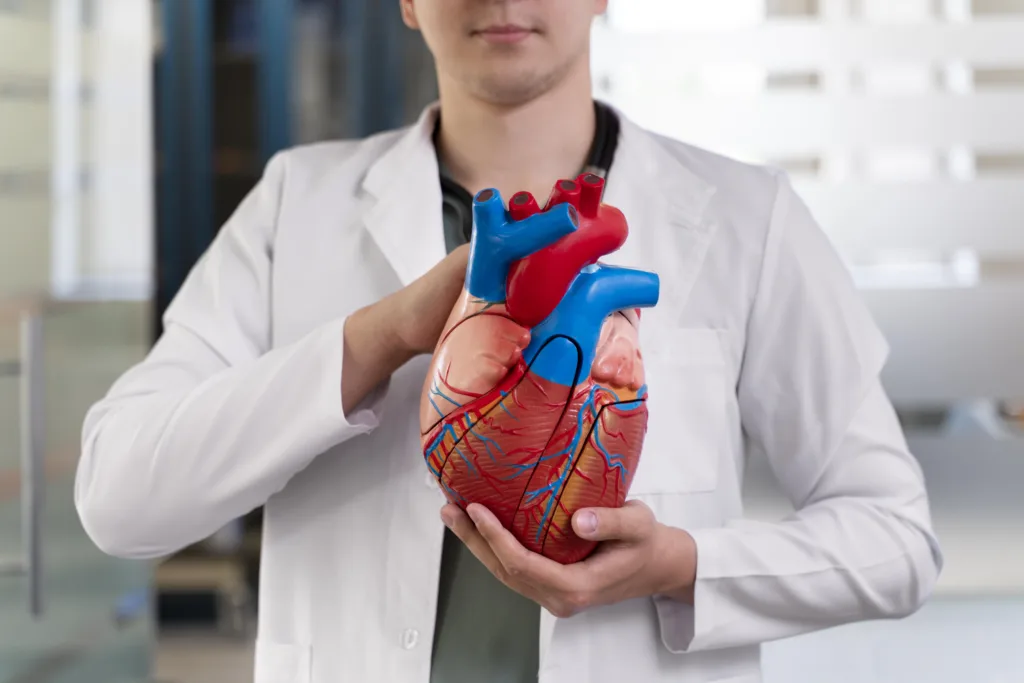

It is crucial for individuals to be aware of the risk factors associated with Myocardial Ischemia and seek timely medical attention to prevent any serious cardiovascular complications. Regular health check-ups and lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing this condition and ensuring better heart health overall. The treatment for Myocardial Ischemia includes improving the blood flow in the heart muscles. This can be achieved through medications, angioplasty (a procedure to open blocked arteries), or bypass surgery.
Table of Contents
Symptoms:
Symptoms of Myocardial Ischemia can vary, and some people may have no signs or symptoms at all, a condition known as ‘silent ischemia.’ When symptoms occur, the most common ones include chest pressure or pain, typically on the left side of the body. Other possible symptoms experienced more often by women, elderly individuals, or people with diabetes, may include:
- Neck or jaw pain
- Shoulder or arm pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath during physical activity
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Fatigue
Causes of Myocardial Ischemia:
Certain lifestyle decisions might increase the risk of having myocardial ischemia even more. The effects of Ischemia can manifest in different parts of the body, affecting various organs and areas.
It can impact the brain, leading to cerebral ischemia, affect the heart, causing myocardial ischemia or ischemic heart disease, affect the legs, leading to severe peripheral artery disease, and even impact the intestines, causing acute mes-enteric ischemia.
Each of these conditions arises due to restricted blood flow to the specific region, leading to potential complications and adverse health outcomes.
Severe and abrupt headaches, sometimes followed by nausea or vomiting, unconsciousness, trouble moving one side of the body (weakness, numbness, or inability to move one side of the face, hands, or feet), and trouble speaking or comprehending others are all signs of cerebral ischemia.
Chest discomfort (angina), fast heartbeats, pain in the neck, jaw, shoulders, or arms, shortness of breath during activity, sudden perspiration, upset stomach, or exhaustion are all signs of ischemia in the heart.
Symptoms of peripheral ischemia in the legs can include cold and weak feet, leg pain, severe pain even at rest, shiny and smooth skin on the legs and feet, and non-healing wounds.
Ischemia can be categorized into different types based on the affected body part.
For instance:
Cardiac Ischemia, also known as Ischemic Heart Disease and Myocardial Ischemia, occurs when there is reduced blood flow and oxygen supply in the heart muscles.
It can be of two types:
Focal Ischemia, which is localized in a specific area of the brain (like a stroke or transient ischemic attack – TIA).
Global Ischemia, which involves larger areas of the brain.
Critical Limb Ischemia is a form of peripheral artery disease where there is reduced blood flow in the legs or arms. Mes-enteric Ischemia occurs when there is reduced blood flow in the intestines. Cutaneous Ischemia results in reduced blood flow in the skin and may cause cyanosis or gangrene.
Other researchers classify ischemia into two main types:
- Thrombotic
- Embolic.
Thrombotic Ischemia:
occurs when there is a blockage in a blood vessel supplying an organ or body part.
Embolic Ischemia:
Embolic ischemia it occurs when a blood clot or plaque from one part of the body breaks off and travels to block a blood vessel in another part of the body.
Image Credits: Image by Freepik
Image Credits: Image by Freepik